1. Introduction
People usually like to consult friends or search on recommendation apps before going to the restaurant where they never go. Because we don’t want to have some risk to eat lousy food and wast money, right?
Yelp review statistics as of December 31, 2018, demonstrated that Yelp had collected 177 million reviews. In 2016, Yelp filtered sixteen percent reviews as spam reviews. Review is crucial because it has a significant impact on our decision. Fraud review could bias customers decision and cause cheating business competition. Therefore, how to effective detect spam or fraud review and tell the user why the review is a suspicious spam review is urgent. The official spam detector does not publish the algorithm in order to prevent spam reviews from finding the vulnerability, however, based on other spam review detector research and official document. The Official detector used many features which others cannot obtain such as user behavior, user location, where the review created, repetitive review and others.
We want the problem to come back to itself, the review. Therefore, our detector almost focuses on the text and borrow star information as side features and trying to determine a spam review based on the writing style. Our contribution:
- Created a useful filter to help remove most-unlikely spam reviews;
- Annotated suspicious spam reviews;
- Based on the pool-based uncertainty sampling active method, we generated a suspicious spam detector;
- Transparency part, to explain why the review is a suspicious spam review;
- Find characteristics of suspicious spam review.
The rest of the article is organized as follows: data set analysis, filtering model, active learning, training model and testing, transparency, and summary.
2. Data analysis
Yelp dataset consisted of three sub-datasets which are ‘user.csv’. ‘business.csv’ and ‘review.csv’. The user information contains user_id, user_name, review_count, useful and other features. In the business dataset, The average business rating and review_count are useful features in transparency and annotation. Review dataset has over five million reviews and has no spam review label. Directly annotate suspicious spam review in review dataset is a waste of time.
Distinguish the spam review is hard, but how to find the most non-spam review is easier. Based on our observation and analysis the dataset, the elite users have the most trustfulness review. Four main reasons can proof our determination:
- Elite users are rare and hard to become;
- Elite users must provide real personal information such as real personal image and real name;
- Other friends must nominate elite users;
- Inappropriate behavior will cause the elite user to lose their elite user title.
3. Filtering model
The idea of filtering model is:
- Elite users’ reviews as training samples;
- Rating as labeling;
- Non-elite users’ reviews as testing samples;
- Find all misclassified reviews.
We used high-speed data structure: Pandas library. Based on the user_id and elite feature tags in ‘user.csv’, we found all elite users’ user_id. After that, search review in the ‘review.csv’ dataset based on the user_id index.
To prevent unbalanced training dataset, each elite user only chooses two reviews. We selected a total of ten thousand reviews depending on five thousand elite users.
Yelp original rating scope from 1.0 to 5.0 and interval is 0.5, so the entire classes are nine. Too many classes will decrease filtering model performance because every user has a different rating baseline. We normalized classes from nine into three sectors which are like: 4.0-5.0, neutral: 3.0-3.5, and dislike: 1.0-2.5.
Tokenizing every review and puts into the logistic regression to train with ‘L2’ penalty, and labeling as normalized classes. After that, predict tokenized non-elite users’ reviews with same countvector. Compare the predicted result with normalized non-users’ review classes. If the prediction is wrong, that means this review has a significant different writing style with the elite review.
Then we use those misclassified reviews as annotation candidates. Here are two reviews found by this filter and we consider they are suspicious review:
- ‘Ceaser’s salad was super salty, pasta and shrimp dish had no taste. Huge portions, no taste.’ useful: [0] funny: [0] cool: [0] stars: 1 business average stars: 4.0 user review_count: [11] user friends: 1 user fans: [1]
- ‘Food was good but service there is not good. This is the second time going there and both times the service was junk.’ useful: [0] funny: [0] cool: [0] stars: 2 business average stars: 3.5 user review_count: [2]
First, those two reviews are short and too general to provide useful information to other users. Besides, bold information are we considered improper features, such as extreme words and strong negative emotion words. Also, the rating from the first user has a high bias with the business average star and the second user only has two reviews. Based on these criteria, we manually annotate data in the next section.
4. Active learning
Build pool-based spam review detector followed by below steps:
- [1.] Check misclassified reviews as candidates;
- [2.] Annotate 20 suspicious spam samples as the first training samples;
- [3.] Annotate 20 elite reviews as the non-spam samples;
- [4.] Logistic regression as training model to train;
- [5.] Label other 20 suspicious spam samples and predict;
- [6.] Choose 15 samples which has the most uncertainty samples as training data;
- [7.] Choose 15 elite reviews as the non-spam samples;
- [8.] Repeat step 4 to 7 until satisfied.
For the feature part, we borrow z-scored bias rating as side feature, the bias rating defined below:
The first step is to calculate the rating distance between a business with the user. After that, get mean and variance distance for all samples. Get each sample z-scored bias rating in the end. Tokenized every sample and contact bias rating features into csr_matrix as our features. Finally, we annotated 57 suspicious spam reviews and 57 non-spam reviews according to checked 441 reviews.
5. Result and transparency
Table 1 shows top 20 spam features and non-spam features. We can find emotional words in spam features like not, very and shit. Also, spam reviews often evaluate the business from price, place, and service perspectives. While non-spam features, mojority features are mild words. The rating bais has the greatest coefficient and even has six times than the second feature. Significant rating bais is a key to distinguish whether tha review is a spam review. However, we do not want the classifier to pay more attention to one feature.
| Spam_fea | Spam_coef | Non_spam_fea | Non_spam_coef |
|---|---|---|---|
| dis_star | 1.7864730423022601 | little | -0.43644293217441404 |
| not | 0.45398365028786114 | like | -0.4186720058050982 |
| and | 0.33555033149532026 | we | -0.41430441313552113 |
| the | 0.30244771815779925 | of the | -0.4108856046445497 |
| service | 0.28174880109781575 | it was | -0.37156178428011205 |
| 12 | 0.2768576767105967 | i like | -0.33252175406732715 |
| to | 0.261459445856917 | that | -0.32824804738028057 |
| it | 0.2525743550474557 | often | -0.324157713611193 |
| price | 0.24548080553941218 | were | -0.3136826697511078 |
| the price | 0.224074530784817 | it’s | -0.300996823374483 |
| this place | 0.21078956122472053 | had | -0.2922864338488543 |
| i ate | 0.205664993694128 | of | -0.2882311690292398 |
| there | 0.2020027219182647 | of the | -0.2851251527232189 |
| a | 0.19835120120135094 | more | -0.27101235568106163 |
| anyone | 0.1946593427834893 | in the | -0.2676366625615579 |
| shit | 0.19372321587078778 | can | -0.2403726732932835 |
| i’ll | 0.19286395394968167 | comes | -0.23119586398216976 |
| now | 0.19061090912766987 | great | -0.22225190957959176 |
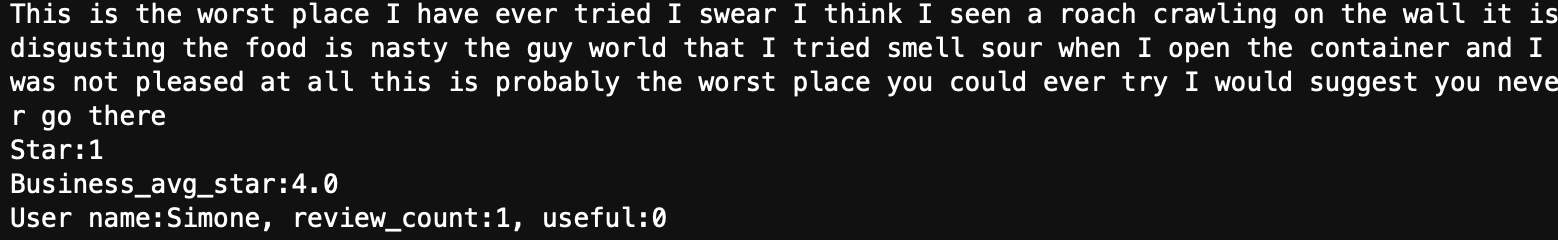
We also examined the top ten confidence spam reviews and top ten confidence non-spam reviews. The result is beyond our expectation. All top spam reviews often appeared extreme emotion vocabulary, suggest other customers never go to the business, two of reviews also recommend viewers to other business, and has a high bias rate. Figure below shows one review from the top spam reviews.
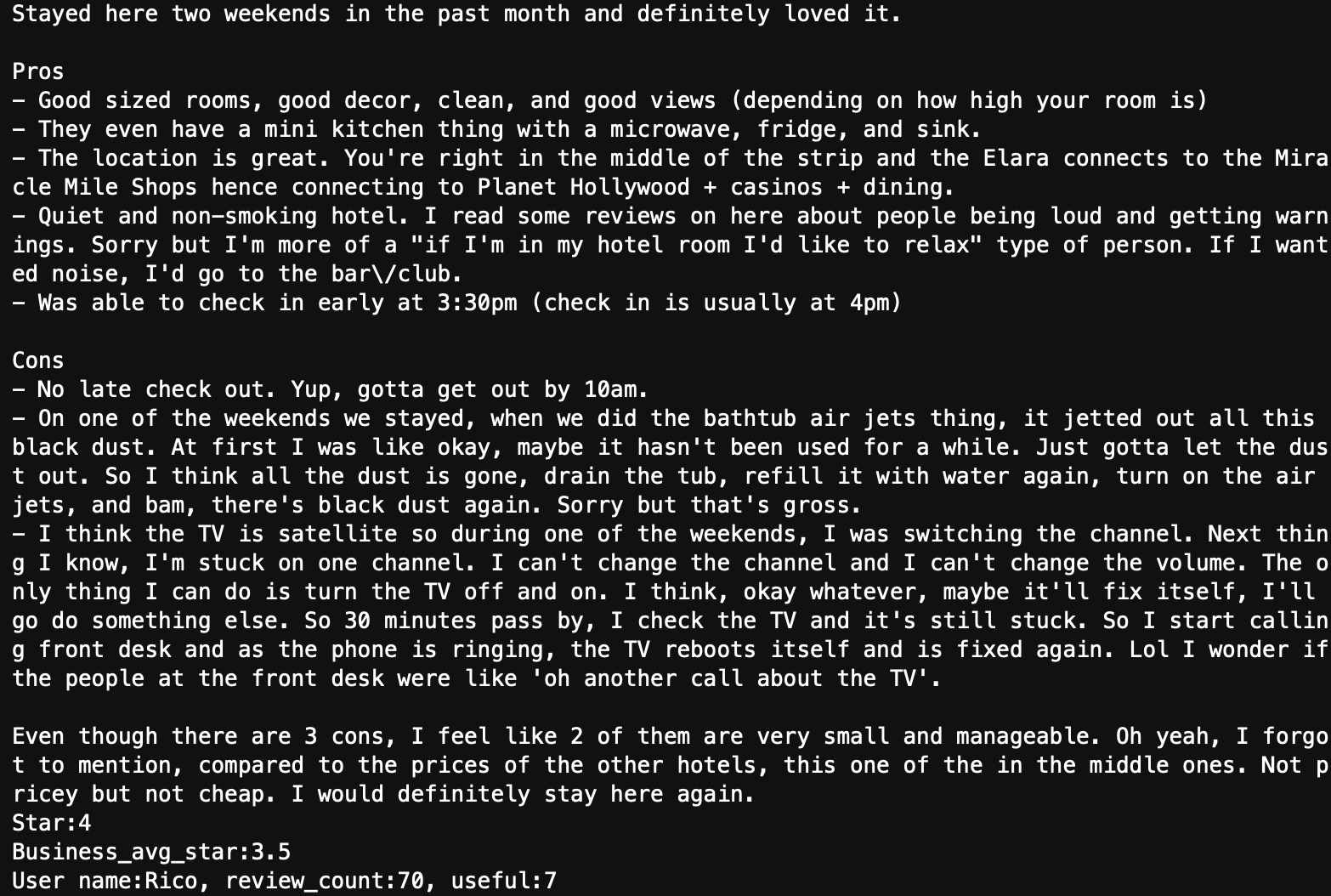
In contrast, the top ten non-spam reviews demonstrate objective evaluation, a wealth of argument, and provides appropriate advice to the business and other users. Below shows one review from the top non-spam reviews.
We have no official label, so the be more precise, we are trying to find suspicious spam review rather than spam review. A suspicious spam review often has:
- Extreme words;
- Significant rating bias with business average rating;
- Useless comments( Too general to evaluate a business);
- Refer other business;
- Short;
- User has a few comments;
- Rare other people think the review is useful, funny or cool.
In the future, we will remove bias rating features and only apply token features. Top features contain many stop words like the, a, it and others. Therefore, filter the stop words. Find official spam label to evaluate the real accuracy.
